Define Phase is the first phase of Lean Six Sigma Project. Following are the deliverable of this phase:
- Develop the Project Charter
- Identify the Project CTQ
- Create Process Maps
Develop the Project Charter
Project Charter is an important document that summarizes the purpose, current scenario & goal, measures of success (CTQ), project’s scope, quantitative & indicative project benefits, and team members. This is the most important document, as it creates a term of reference for this entire Lean Six Sigma project. In order to prepare the project charter, several meetings and preparatory steps may be needed. In some cases, gathering the Voice of Customer (VOC) may be required to even understand the problem. Project Scoping determines exactly how the project will contribute to overall business, whether the efforts will be diverted to maximum impact area, team composition, financial resources required, etc. In Six Sigma, a tool called ‘In-Frame Out-Frame’ is used to decide on the scope. Six Sigma Green Belt should closely work with the Project Sponsor to complete the Project Charter.
Identify the Project CTQ
CTQ refers to Critical to Quality metric. This is a measure of success for the project. Usually, there is only one CTQ for DMAIC projects. It can either be a measure of efficiency or effectiveness. However, it is a key performance indicator for Voice of Customer or Voice of Business. Further, it should be measurable. Usually, its indicative or accurate current performance is reported in the project charter. The above two deliverable run parallel, and they are of significant importance because they mark the formal kick-off of the project, team member induction, Lean Six Sigma training (if not included earlier).
Create Process Maps
In order to understand the end-to-end process; a detailed process document is created by the team. However, in case such documentation already exists, then it becomes easy for the project team members to revisit it.
Six Sigma Green Belt can involve all her team members in this activity. Two best ways of mapping a process are to interview all the parties involved in the process or to conduct a work-out session with all parties. Latter requires good facilitation skills. Once the process maps have been created, the team can use them to identify the bottlenecks, challenges, issues, inputs & outputs, delays, etc. Essentially, it can be used to decide which part of the process is important, and needs to be introspected. On completion of the above deliverable, a formal define tollgate review is conducted. Then the project moves to Measure Phase.
Control phase is the fifth and final phase of Lean Six Sigma projects. Following are the deliverable of this phase:
- Prepare Control Plan
- Final Implementation
- Establish Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Benefits Computation & Closure
Prepare Control Plan
Control Plan or Process Management Plan is a document ensuring that a robust mechanism to monitor and follow-up is established before the solution is implemented. Most Lean Six Sigma projects don’t exist after a few years of implementation. Usually, it is because of a poor control plan. A control plan covers: which metrics will be monitored, method of monitoring, how often, by whom and what has to be done when they go out of control (aka Reaction Plan).
Final Implementation
Establish Statistical Process Control
As a part of the control plan, the method of monitoring has to be specific. Statistical Process Control uses well known Control Charts or Shewhart Charts. A control chart, computes the lower and upper control limits as a threshold to monitor any process measures; like CTQ. As the threshold is breached, the reaction plan has to be triggered. As the name suggests, it is a chart that is based on the principles of statistics, and hence there are no false alarms. Instilling the discipline of creating control charts and monitoring as per Control Plan is part of the rigor of a Lean Six Sigma Green Belt.
Benefits Computation & Closure
The last deliverable of the Lean Six Sigma project is Benefits Computation and Closure. But before that, the project is monitored for enough time (2 weeks to 2 months) to ensure that benefits are sustained. When the Lean Six Sigma Team is satisfied with the results, then the improved process is formally handed-over to the process owner. Financial and non-financial benefits are computed based on actual results, and a formal sign-off from the finance manager and sponsor is obtained. This will be the project closure. The Lean Six Sigma team celebrates its success; distributes rewards for active team members; and finally the Six Sigma Green Belt Certification Ceremony is undertaken.
As a business analyst you are often expected to act as a bridge between a functional domain and the business stakeholders. Business analysts must be great verbal and written communicators, tactful diplomats, problem solvers, thinkers and analyzers. Though you have been extensive training in project management and related areas, using systematic business and management tools such as graphical analysis, data distribution & visualization, statistical discovery, etc are considered to be difficult by many Business Analysts.
Fortunately Lean Six Sigma, which is process improvement methodology provides many of the tools that can be handy for Business Analysts at one place. It comprises of statistical tools and techniques along with visualization tools. There are many tools such as Visual Analysis & Data Discovery tools like Fish-bone, 5 why, in scope-Out scope, Box plots and analytical tools like MSA, Descriptive Statistics, Variation, Correlation and Regression. They are explained in brief as under: Visual Tools: There are many tools which a business analyst will learn from Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification. We’ll talk about few Visual analysis tools from Lean Six Sigma in brief as under:
- Fish Bone Diagram also called as Cause and Effect Diagram helps to reach the root cause of any business issue. The important characteristic of this tool is to categorize the issue into 6 different aspects like Men, Machine, Material, Measurement, Method and Mother Nature (Environment). This will help the analyst prioritize the problem and solve the problem in a systematic manner.
- Another tool for root cause analysis is 5-Why which involves repeating the question “Why” where each question forms the base of the next question and this will go on until the root cause is found. All the questions and answers of the 5 Why, are placed on a sheet of paper with the help of which the analyst can view the whole picture in a single page.
- Box plot is a quick way of visualization of data and is represented in the form of box & whiskers. It helps in scrutinizing and comparing sets of data which demonstrates the variation in the sample data set.
- Statistical process control (SPC) is method of measuring and controlling KPIs of any process. AKA control charts, this helps to proactively identify issues from data. It is a great tool for continuous monitoring of process parameters both in service and manufacturing processes.
- Run charts are similar to control charts and suggest shifts in the process over a period of time and points out special factors which influence the process variability.
- FMEA stands for Failure Modes and Effect Analysis which is an approach to identify all possible failures in any process. Like doing analysis of how and where we can fail so as to take precaution before even starting the implementation of any project. This is a very important element for the success of any project which will help a business analyst in his/her daily management.
Analytical Tools: Here are few examples of data discovery analytical tools that a Business Analyst will learn from Six Sigma.
- Quite often Business Analysts struggle with poor data quality. MSA aka Measurement System Analysis is a Lean Six Sigma tool used to evaluate that whether the data collection method, the instruments/source used for measuring and whole measurement is precise & accurate or not. This is also used to ensure the integrity of data used for analysis and gauge the effects of errors in measurement used to make decisions taken for product or processes.
- Descriptive statistics includes the assessment of central tendency and measures of dispersion in the any data set. Further it helps to identify skewness, kurtosis, outliers, and specific patterns in the distribution.
- Analysis of Variance abstracted as ANOVA is a statistical hypothesis test used to identify significant factors that cause a particular business issue. The biggest the merit of such advanced statistical methods is in confidence & credibility that a Business Analyst can provide to the leadership and management on his analysis and conclusions.
- Correlation & Regression are similar tools used to establish a relationship between the two business variables such as revenue and capacity. By validating such relationships, the Business Analyst can bring out significant insights to the management.
A business analyst having Green Belt Certification shall have a comprehensive understanding of Lean six sigma and shall be able to apply its tenets to their daily work. The principles of Six Sigma are so widely applicable that employees getting trained are highly valued and aggressively sought after. Lean Six Sigma Certification will be a stepping stone for professionals to a higher level as you avail expertise in different problem solving tools and techniques of Lean Six Sigma.
As we all know that there are different levels of certification in Lean Six Sigma and these levels have been associated with “Belt” titles. It’s a very obvious question that why the levels here have been associated with the titles used in Martial Arts? That is because of the association of discipline and rigor in Lean Six Sigma similar to the martial arts. You would find four commonly used belt titles in Six Sigma Certification and they are Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt and Master Black Belt. However, the most basic level in Lean Six Sigma is sometimes called as “White Belt”. A White Belt understands the theoretical aspects but virtually no application knowledge of the Lean Six Sigma concept. One could say this is an entry level awareness program. Let us understand one by one, the four belts mentioned above.
- Yellow Belt: A Yellow Belt is someone who has undergone a basic training program that is may be a day’s training with a basic level of understanding of the quantitative part of the concept. He or she is able to appreciate the goals of Lean Six Sigma. Having knowledge of Yellow Belt level means that person is able to apply basic tools in the company and undertake simple improvement projects. Usually the organization who wants to implement Lean Six Sigma wants all their employees to be at least Yellow Belt trained as this makes the implementation and change management easier and faster.
- Green Belt: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt receives a training of at least one week with emphasis on DMAIC method and tools. DMAIC is problem solving methodology which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve,and Control through which he/she is able to undertake improvement projects in his/her process which improves customer satisfaction and efficiency of the process. Green Belts are also called as “Work Horses” having the following responsibilities:
- Initial analysis of company like Gemba Walk and Data Analysis which will be helpful in defining the road map of the project.
- Define the project and prepare the project charter.
- All over co-ordination with management, yellow belts, black belts and master black belts.
- Facilitate the team through all phases of the project.
- Provide training to the team for effectiveness of the implementation.
- Black Belt: A black belt is someone who receives at least 3 to 4 weeks of extensive training with the emphases on DMAIC method and tools which is explained as above. Unlike a green belt, black belt is a full time role who has the responsibility to run large scale high impact improvement projects where he mentors and coaches green belts. Responsibilities of a black belt are listed as under:
- Helps in deciding the project.
- Helps in refining the project charter and makes sure that the things are moving in the desired direction.
- Leads, mentors and coaches green and yellow belts and champions.
- Empowers the team members to design experiments and analyse the data required for the project.
- Provide training in tools and team functions to project team members.
- Makes sure that the project succeeds.
- Maintains balance between Management, Employees and Customer’s needs.
- Manages the team for effectiveness and efficiency.
- Master Black Belt: It is usually a leadership role having excellent change management skills along with having good technical knowledge. After completion of the black belt course and having good experience he/she receives additional 3 to four weeks of training mostly around change management and statistics. MBB’s primary role is to deploy six sigma concepts in the organization, advice to executives or business unit managers, and leverages, his/her skills with projects that are led by black belts and green belts. A Master Black Belt reports the senior or top management and coaches the black belts and Green Belts. Responsibilities of Master Black Belts are enumerated as under:
- Provides guidance to senior executives and top level managers on Six Sigma management.
- Help identify and prioritize key project areas in keeping with strategic initiatives.
- Continually improve and innovate the organization’s Six Sigma process.
- Apply Six Sigma across both operations and transactions-based processes such as Sales, HR, IT, Facility Management, etc.
Have you ever confronted a situation doing hard work the whole day and at the end you realize that most of the time had been given by you and your team to the Non Value Added things!
- This principle was developed in the year 1896 and is named after Vilfredo Pareto who was an Italian engineer, sociologist, economist, political scientist, and philosopher.
- Pareto derived this concept by his work and experience and observed that 80% of the wealth in Italy belonged to 20% of the people.
- In the year 1941, Dr, Joseph Juran who was an evangelist of quality and quality management as he was an engineer and a management consultant cam across the concept of Pareto Principle. He then started applying the principle in the quality and derived a phrase through experience that is “there are vital few and useful many”.
- The Pareto Principle can be implemented in many different aspects such as in science, management, business, in software, in sports, occupational health and safety, financial service industry, and implementing projects which says that put 80% of your time in 20% of your project which will save a lot of your time and energy.
- Pareto principle can be graphically represented by Pareto Chart that contains bothbars and a line graph, where individual values are represented in descending order by bars, and the cumulative total is represented by the line.
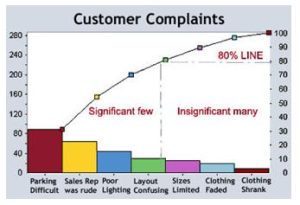 Our Online Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification course teaches you step by step procedure to construct a pareto chart, different pareto variants and how to interpret them. More importantly it covers when and when not to apply pareto principle.
Benefits of Pareto Analysis:
Our Online Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification course teaches you step by step procedure to construct a pareto chart, different pareto variants and how to interpret them. More importantly it covers when and when not to apply pareto principle.
Benefits of Pareto Analysis:
- Improved Decision Making: With a focus on resolving problems, the procedures and processes required to make the changes should be documented during a Pareto analysis. This documentation will enable better preparation and improvements in decision making for future changes.
- Increased Efficiency: Once the changes or problems are listed, they are ranked in order from the biggest to the least severe. The problems ranked highest in severity should become the main focus for problem resolution or improvement. Focusing on causes and problem resolution contributes to organizational efficiency.
- Enhanced Problem Solving Technique: Members of a group can conduct a Pareto analysis together. Arriving at a group consensus about the issues that require change fosters organizational learning and increases group cohesiveness. Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification course shall help the individuals of the company learn many tools along with Pareto Analysis which shall also help him or her to boost their careers.
- Saves Time and Money: Doing right things at the right time with right people and at the right place is naturally going to save time and money and this has to be calculated by multiplying the time with the number of individuals involved in the process.
Sign-up for collaborat newsletter

