The Six Sigma is an approach to business process improvement and performance management which encompasses a statistical and method-driven process. In order to effectively deploy the process in your organization, it is necessary to identify the basic elements that drive the Six Sigma methodology. Knowledge of the Six Sigma fundamentals is the first step toward a successful Six Sigma implementation. Before applying any business strategy in an organization, you must identify the goals and benefits of the strategy. You must also recognize the need for such a business strategy in the organization.
Surviving in a business world that is full of competition is crucial to any organization. Six Sigma provides the means to handle declining product prices in the market, which helps any organization compete with the best companies in business. It targets zero defects by setting a common performance goal for the entire organization. Six Sigma helps an organization achieve increased profitability and quality improvement rates, ahead of any of its competitors. Reduced scrap-related costs, rework, improved yield, and increased customer satisfaction are identified in companies striving to achieve Six Sigma.
A Six Sigma initiative differs from other quality improvement methodologies because it ensures that the costs involved in implementation are offset by the gains received from improvements.
The primary goal of Six Sigma is to implement a measurement-based strategy in an organization that concentrates on process improvement and reducing variation. In addition to this, the other important goals of Six Sigma include:
- Reducing the number of defects, leading to the improved quality of a product or service.
- Achieving customer satisfaction by ensuring that customer expectations are met.
- Reducing cycle time, which enables the faster delivery of products.
- And, higher profitability by improving efficiency and effectiveness of the organization.
In the Define phase, the Six Sigma team in a software product development company found that customers identified many issues in the beta version of its software.
However, if all the issues raised were to be fixed, timelines would slip and the budget would increase. The team then calculated the number of changes and the time and budget required for fixing these issues in the Measure phase.
In the Analyze phase, the team determined if the changes were aligned with the scope of the project and then identified changes that should be made. It also identified conflicting changes pointed out by the reviewers, communication gaps between the developers and the customers, and ways in which changes were communicated to the developers as other major causes of the issues.
In the Improve phase, the Six Sigma team took several steps, such as determining the limitations of the software, having regular meetings with customers, identifying the appropriate application to communicate the changes to the developers, creating change requests, and monitoring the implementation of the approved changes until closure to eliminate the issues.
Finally, appropriate mechanisms were set up in the Control phase to monitor the regularity of meetings and communication between the developers and customers as well as to monitor the performance and usage of the change request feature.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a structured approach followed by customer-driven organizations to transform customer requirements into their product specifications.
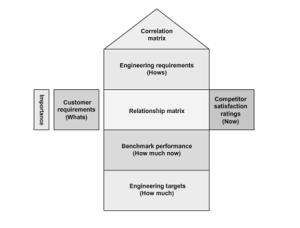 The House of Quality (HOQ) is a diagram used by a product development team during the initial stage of the QFD process.
The House of Quality (HOQ) is a diagram used by a product development team during the initial stage of the QFD process.
It uses a planning matrix to define the relationship between customer requirements and the capability of the product and the company to satisfy these requirements. Because this matrix looks like a house, where customer requirements and product attributes resemble the main living quarters, competitive analysis resembles the porch, and the correlation matrix resembles the roof, it is called House of Quality.
HOQ encompasses different QFD elements used for understanding customer requirements and aligning business processes to meet these customer requirements.
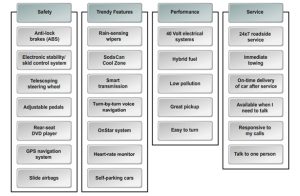
It starts with customer requirements. The customers for a product or service are identified and their requirements from the product or service are gathered using different tools such as focus groups, surveys, and customer experiences. A structured list of customer requirements is then drawn by analyzing and organizing this data using tools such as affinity diagrams and tree diagrams.
Importance ratings are used for quantify the customer requirements and rated according to their importance on a scale of 1 to 5. This rating will be used in the relationship matrix at a later stage.
Another element is the Competitive analysis where customers views about the competition are gathered through research to provide a better understanding of the market. Here, the customers rate an organization’s products or services against competitors’ products or services. Also, Technical requirements that are not known to customers are identified and documented. These requirements generally stem from management or regulatory standards that a product must meet.
Relationship matrix defines the relationship between customer requirements and an organization’s ability to meet those requirements is determined. The relationship between the two factors is classified as weak, moderate, or strong and given the values of 1, 3, and 9, respectively. Even, in Importance weighting rating, Customer requirements are weighted according to their importance for defining and prioritizing key criteria. The relative importance of customer needs and the company’s and competitor’s performance are taken into account while calculating this. Target values for each product or service attributes, known as technical descriptors, that can be used as benchmarks against competitors’ target values are established. These target values are the “how much” of these product or service attributes.
The technical descriptors are compared with the competitors’ technical descriptors using scientific analytical techniques to assess their properties is called Engineering analysis. This also includes reverse engineering competitors’ products or services to determine the values for their technical descriptors. Correlation matrix is the relationship among customer requirements are analyzed to identify correlated requirements. The relationships are then ranked for determining areas of improvement that need to be focused upon.
An affinity diagram is a tool that is used to organize a large number of ideas, opinions, and issues and group them based on their relationships. Affinity diagrams are generally used for categorizing ideas that are generated during brainstorming sessions and can be particularly useful for analyzing complex issues.
The steps for creating an affinity diagram can include:
- Generating ideas through brainstorming.
- Displaying the ideas randomly.
- Sorting the ideas into groups.
- Creating header cards for each group to capture the essential links among the ideas in each group.
- And, drawing the affinity diagram by writing the problem statement at the top and the headers with their respective groups of ideas below the problem statement.
- An affinity diagram helps in sorting and grouping customer requirements.
Sign-up for collaborat newsletter